Alternator Wiring Diagrams are essential tools for mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the electrical connections within the alternator system, helping users to understand how power is generated and distributed in their vehicles.
Why Alternator Wiring Diagrams are Essential
Alternator Wiring Diagrams are essential for several reasons:
- They help users understand the various components of the alternator system.
- They provide a clear overview of the electrical connections and wiring configurations.
- They assist in diagnosing and troubleshooting electrical issues within the alternator system.
How to Read and Interpret Alternator Wiring Diagrams
Reading and interpreting Alternator Wiring Diagrams can be daunting for beginners, but with a little guidance, it becomes much easier:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the key components of the diagram, such as the alternator, battery, and various connectors.
- Follow the flow of electrical current from the alternator to the battery and other components.
- Pay attention to the color codes and symbols used in the diagram to identify different wires and connections.
Using Alternator Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting
Alternator Wiring Diagrams are invaluable when it comes to troubleshooting electrical problems. Here’s how you can use them effectively:
- Identify the specific area of the alternator system that is causing the issue by following the wiring diagram.
- Check for loose connections, damaged wires, or faulty components based on the information provided in the diagram.
- Use a multimeter to test the voltage and continuity of the electrical circuits as outlined in the diagram.
Safety is paramount when working with electrical systems and using wiring diagrams. Here are some safety tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent the risk of electric shock.
- Avoid working on electrical systems in wet or damp conditions to minimize the risk of short circuits.
- Use insulated tools and wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety goggles, when handling electrical components.
Alternator Wiring Diagram
8em2004 Alternator Wiring Diagram
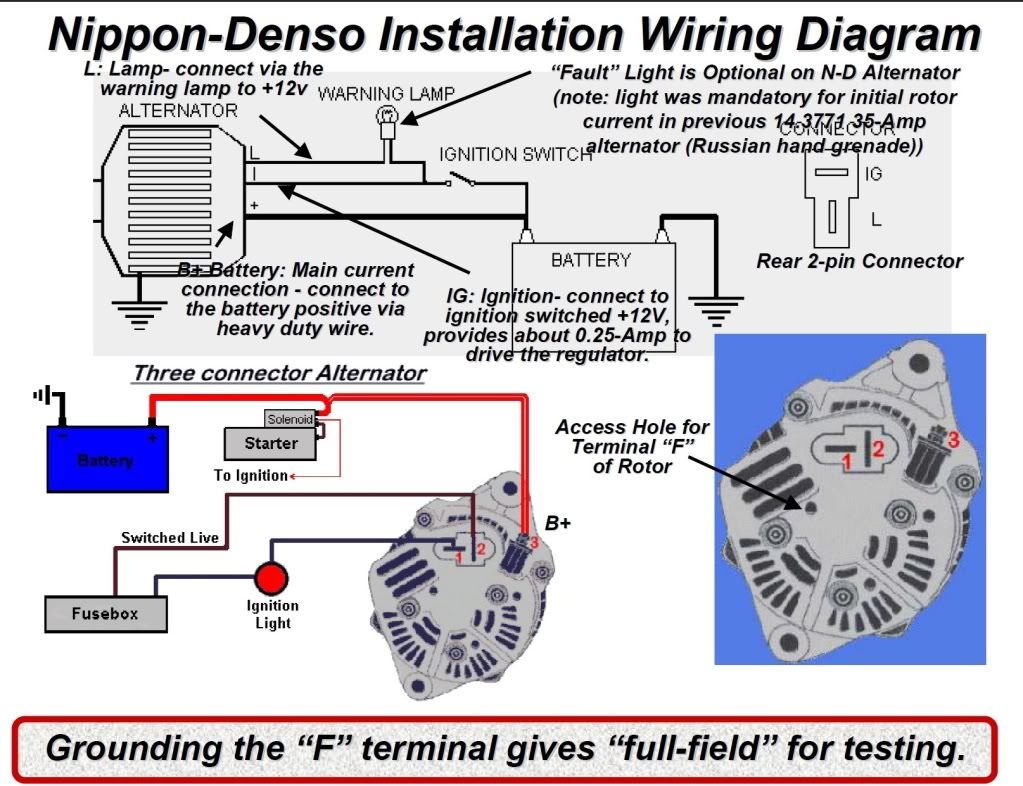
[2 Wire, 3 Wire, and 4 Wire] Alternator Wiring Diagram – Drill and Driver
![Alternator Wiring Diagram [2 Wire, 3 Wire, and 4 Wire] Alternator Wiring Diagram - Drill and Driver](https://i1.wp.com/www.drillanddriver.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/4-wire-alternator-wiring-diagram-2.jpg)
Alternator Connection Diagram – Headcontrolsystem

Alternator Delco Style 22s1 Wiring Diagram – Wiring Diagram Pictures

vw alternator wiring
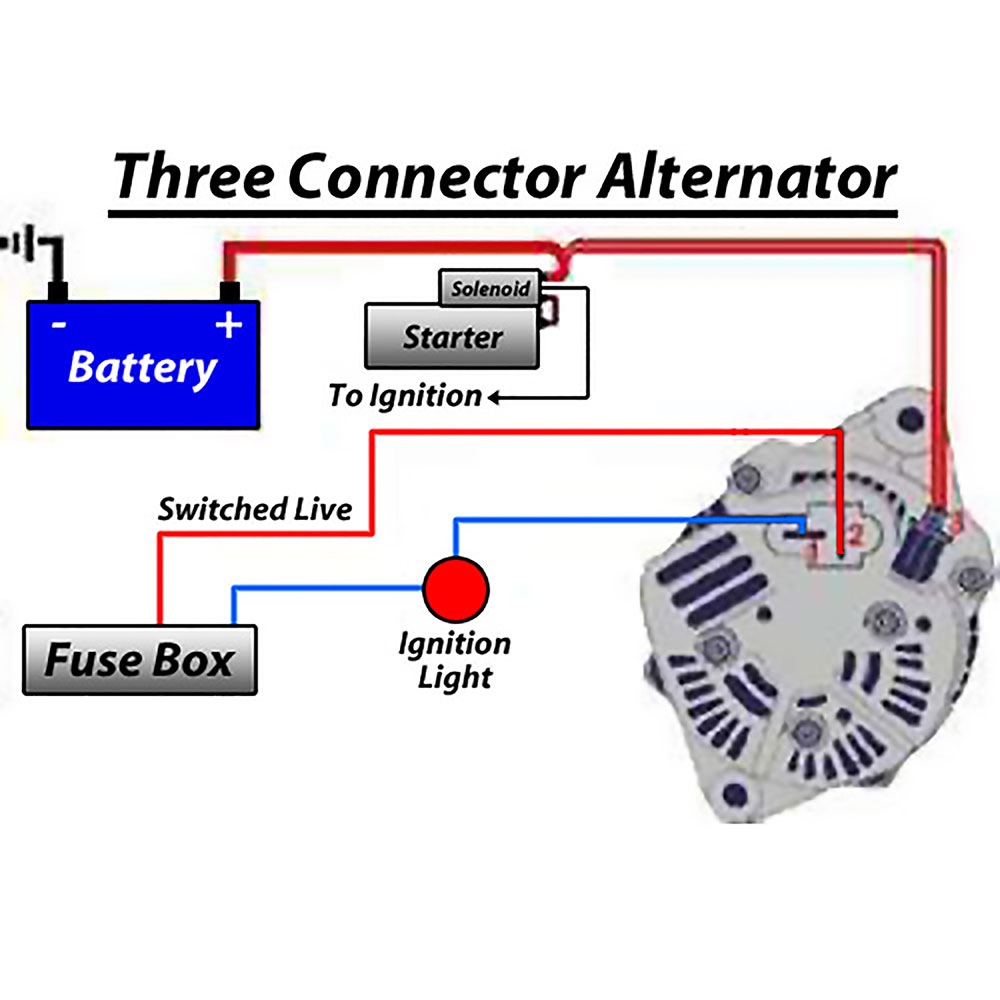
[18+] How To Wire A Chevrolet Alternator, Vehicle Alternator Wiring Diagram
![Alternator Wiring Diagram [18+] How To Wire A Chevrolet Alternator, Vehicle Alternator Wiring Diagram](https://i1.wp.com/i.pinimg.com/736x/88/5b/81/885b81e7558a8eb81806bc92ee85e97e.jpg)