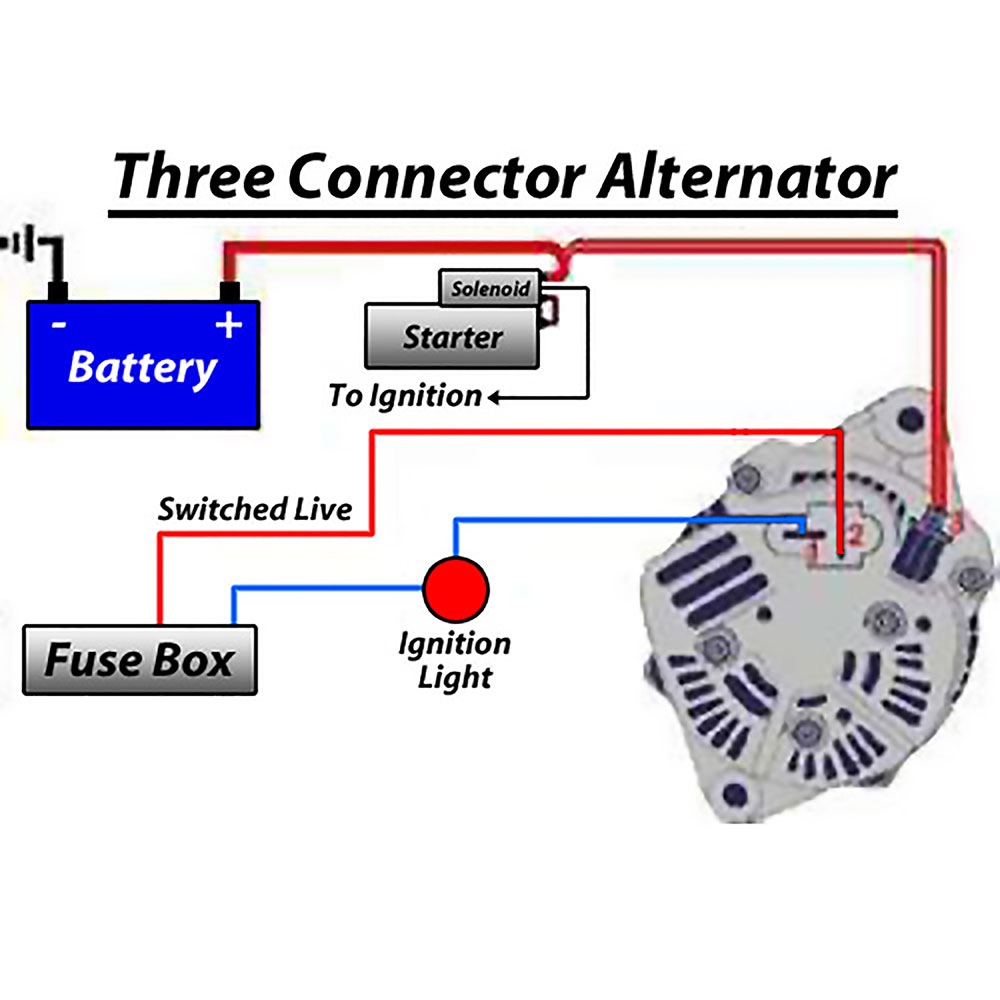
Basic Alternator Wiring Diagrams are an essential tool for anyone working on automotive electrical systems. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the wiring and connections within the alternator system, helping mechanics and DIY enthusiasts understand how the various components work together.
Why Basic Alternator Wiring Diagrams are Essential
Understanding the wiring diagram of an alternator system is crucial for several reasons:
- Identifying the various components within the system
- Understanding how the components are connected
- Troubleshooting electrical issues effectively
- Ensuring proper installation and maintenance of the alternator system
How to Read and Interpret Basic Alternator Wiring Diagrams
Reading and interpreting a basic alternator wiring diagram may seem daunting at first, but with a little practice, it becomes second nature. Here are some tips to help you navigate these diagrams effectively:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the key symbols and color codes used in the diagram
- Follow the flow of the wiring, from the battery to the alternator and back
- Pay attention to the connections between components, such as the voltage regulator and diodes
- Refer to the legend or key provided in the diagram for additional information
Using Basic Alternator Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting
Basic alternator wiring diagrams are invaluable when it comes to troubleshooting electrical problems in your vehicle. By referencing the diagram, you can:
- Identify potential issues with the wiring or connections
- Locate faulty components that may be causing the problem
- Verify proper voltage and current flow within the system
- Assist in making repairs or replacements as needed
Importance of Safety When Working with Electrical Systems
When working with alternator wiring diagrams or any electrical system, safety should always be a top priority. Here are some important safety tips to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components
- Use insulated tools to prevent shock hazards
- Avoid working on electrical systems in wet or damp conditions
- If you are unsure or uncomfortable with electrical work, seek professional help
Basic Alternator Wiring Diagram
Simple 12v Alternator Wiring Diagram

[2 Wire, 3 Wire, and 4 Wire] Alternator Wiring Diagram – Drill and Driver
![Basic Alternator Wiring Diagram [2 Wire, 3 Wire, and 4 Wire] Alternator Wiring Diagram - Drill and Driver](https://i1.wp.com/www.drillanddriver.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/4-wire-alternator-wiring-diagram-2.jpg)
Alternator Circuit Explained : 12 Volt Alternator Wiring Diagram
inside my 01 honda alternator diagram – Wiring Flow Line

Simple 3 Wire Alternator Wiring Diagram

Technical – Understanding alternator wiring | The H.A.M.B.
